When we hear about high or low blood sugar we might associate it to one of a few things like diabetes, low energy or sugar cravings. Many might mistakenly assume that the only people with “blood sugar issues” are diabetics. Let’s dispel that myth and generate a better understanding of what blood sugars are and how they can contribute to optimal health or if unmanaged, can lead to chronic disease.
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, but when it becomes imbalanced—either too high or too low—it can lead to a plethora of health issues. Understanding what blood sugars really are, how our lifestyle affects them and what happens when they are out of balance is not only important for preventative health, but crucial when looking to improve it.
The Importance of Balancing Blood Sugar
Blood sugar levels naturally and normally fluctuate throughout the day. Their fluctuation is influenced by things like the food we eat, our physical activity, and even our stress levels. While fluctuations are normal, if they become extreme or chronic, they can lead to significant health problems.
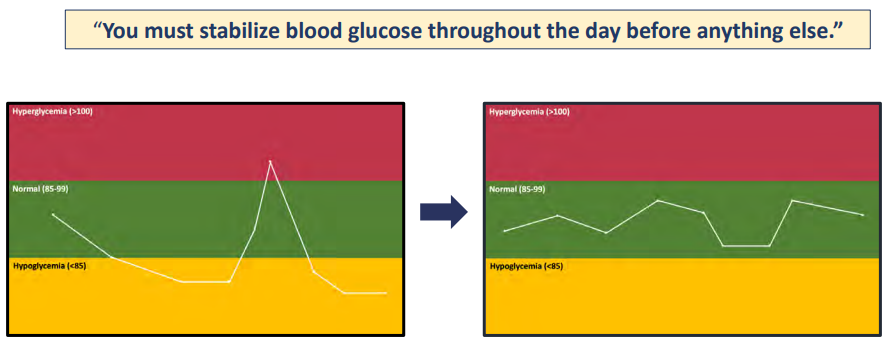
Balanced blood sugar levels are essential for maintaining consistent energy, stable mood, cognitive function, and overall metabolic health. When blood sugar is balanced, the body can efficiently use glucose for energy, reducing the risk of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes.
What Causes the Fluctuations of High and Low Blood Sugar?
High Blood Sugar (Clinically referred to as Hyperglycemia):
Hyperglycemia occurs when there is too much glucose in the blood. This can happen for several reasons:
- Dietary Choices: Consuming high amounts of refined carbohydrates and sugars leads to rapid spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Insulin Resistance: When cells become resistant to insulin, the hormone responsible for allowing glucose to enter cells, blood sugar levels remain elevated.
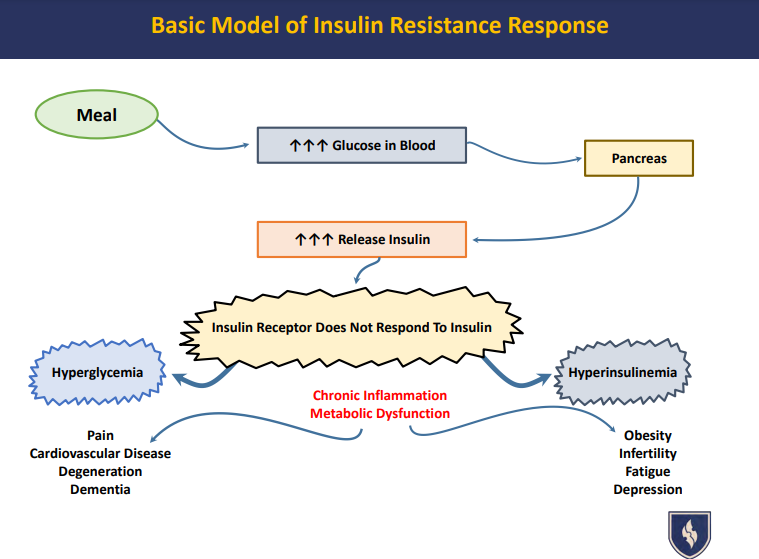
- Stress: Stress hormones like cortisol can increase blood sugar levels by prompting the liver to release more glucose into the bloodstream.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and decreased insulin sensitivity, both of which contribute to hyperglycemia.
- Chronic Inflammation: Inflammatory processes in the body can disrupt normal glucose metabolism, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
Low Blood Sugar (Clinically referred to as Hypoglycemia):
Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low, typically below 70 mg/dL. Causes include:
- Skipping Meals: When meals are skipped or delayed, glucose levels can drop, especially in people with diabetes or those who are insulin-sensitive.
- Overproduction of Insulin: In some individuals, especially those with insulin resistance or certain pancreatic conditions, the body may produce too much insulin after eating, leading to a sharp drop in blood sugar.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can cause blood sugar levels to drop, particularly if consumed on an empty stomach.
- Intense Physical Activity: While exercise is beneficial for health, very intense or prolonged activity without adequate nutrition can deplete glucose levels.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, especially those used to treat diabetes, can cause blood sugar to drop too low.
Are There Serious Negative Effects of Imbalanced Blood Sugar?
Imbalanced blood sugar, whether high or low, has wide-reaching effects on health.
Hyperglycemia:
- Damage to Blood Vessels: Chronically high blood sugar can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular diseases like hypertension, heart attack, and stroke.
- Nerve Damage: High blood glucose levels can damage nerves, causing a condition known as diabetic neuropathy, which can lead to pain, tingling, or loss of sensation, especially in the hands and feet.
- Kidney Damage: Over time, high blood sugar can damage the kidneys’ filtering system, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Vision Problems: Hyperglycemia can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy and potential blindness.
- Weakened Immune System: High glucose levels can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Hypoglycemia:
- Cognitive Impairment: Low blood sugar can impair brain function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
- Mood Swings: Hypoglycemia can cause irritability, anxiety, and other mood disturbances due to the brain’s sensitivity to low glucose levels.
- Fatigue: Lack of glucose deprives the body of its primary energy source, leading to feelings of exhaustion.
- Seizures: Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures and even coma if not promptly treated.
So yes, there is a serious negative impact for living with chronic blood sugar imbalances and they fall like dominoes and collect like dust. Your body will feel the effects pile up if nothing is done to manage your blood sugar. How do you know if your blood sugars are imbalanced?
Signs and Symptoms of Dysregulated Blood Sugar
Recognizing the signs of dysregulated blood sugar is eye opening and empowers you to make more intentional lifestyle choices. What might be some symptoms of an imbalance?
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue, weakness, low energy, chronic fatigue syndrome
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent infections
- Shakiness or trembling
- Sweating
- Rapid heartbeat
- Hunger, even after eating
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Anxiety or nervousness
- Sugar/carb cravings
- Weight fluctuations/weight loss
- Mood swings, nervousness or “jitteriness”
- Blurred, worsening vision
- Slow healing of skin wounds, dryness, cuts and bruises
- Heavy breathing and trouble exercising
- Tension headaches
- Fatigue after meals
- Impaired brain function after meals
- Chronic inflammation throughout the day
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty exercising, but significant improvements in energy after exercise
Determining if blood sugars might be an issue for you:
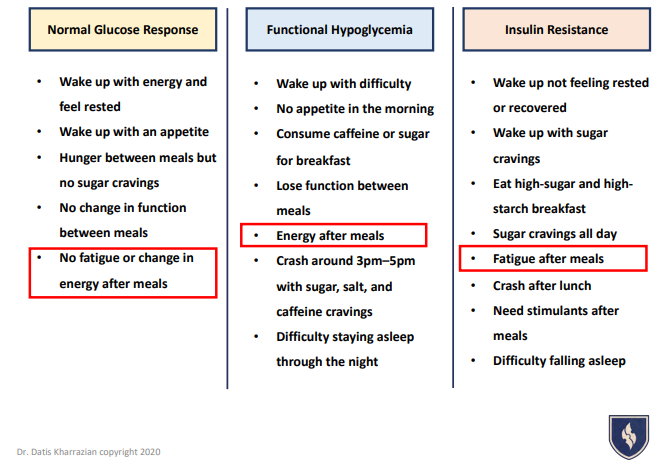
Blood sugars are the only cause of signs like this, but because the body works like a puzzle, one piece locking into another, you can be certain that if you are experiencing a handful or more of these symptoms then blood sugars are probably a piece of your puzzle needing attention.
Chronic Disease is an Inevitable Result of Imbalance
As the puzzle pieces become tattered, the dominos begin to fall into each other and symptom after symptom occur. The other puzzle pieces of the body feel the result of the imbalance of another. When this happens, we begin to see chronic disease occur.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Prolonged hyperglycemia can lead to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Long-term high blood sugar can cause kidney damage, eventually leading to chronic kidney disease and potential dialysis.
- Retinopathy: Persistent high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage due to high blood sugar can become permanent, leading to chronic pain, numbness, or even amputation in severe cases.
- Cognitive Decline: Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia have been linked to cognitive decline and an increased risk of developing dementia.
You have the Power in your Hands: Dietary and Lifestyle Interventions
None of this is to scare you, but to make you aware. The more you understand about your body, the better you will be able to take care of it. Balancing blood sugar is achievable through a combination of dietary and lifestyle interventions. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. Emphasize Whole Foods:
A diet rich in whole foods, high protein, high fiber and healthy fats provide a steady supply of nutrients which helps regulate blood sugar levels. Make sure each meal includes a good balance of protein, fat, and fiber in every meal to slow the absorption of glucose and prevent blood sugar spikes. This combination helps in maintaining steady energy levels throughout the day.
2. Limit Refined Carbohydrates and Sugars:
Reducing intake of refined sugars and processed foods can prevent spikes in blood sugar. Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, which are digested more slowly, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Avoid eating “naked” carbs. Meaning, pair it with a protein and fat. Starting out, you might exclude sweets, starches and fruits all together.
3. Incorporate Regular Physical Activity:
Exercise helps to increase insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to use glucose more effectively. Aim for a mix of aerobic exercises, like walking or swimming, and strength training to maintain muscle mass, which helps regulate glucose metabolism. You’ll want to avoid overtraining.
4. Practice Stress Management:
Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can disrupt blood sugar balance. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and improve blood sugar regulation.
Poor sleep can negatively impact insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support overall metabolic health.
6. Stay Hydrated:
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Water helps to dilute glucose in the bloodstream and supports the kidneys in flushing out excess sugar.
7. Limit Alcohol, Caffeine and Nicotine Intake:
Alcohol and caffeine can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, especially when consumed on an empty stomach. Moderation is key, and it’s best to consume alcohol with a meal to mitigate its effects on blood sugar.
8. Consider Herbal Supplements:
Certain herbs and supplements, such as cinnamon, berberine, and chromium, have been shown to support blood sugar regulation. However, these should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Balancing blood sugar is truly a cornerstone of good health, impacting everything from energy levels to long-term chronic disease risk.
Breakfast Recipe that is Blood Sugar Balancing
A great breakfast recipe that is high in protein, fiber, and includes healthy fats is Quinoa and Spinach Breakfast Bowl with Avocado and Eggs.
Ingredients:
- 1/2 cup cooked quinoa (protein, fiber)
- 1 cup fresh spinach (fiber, vitamins)
- 1/4 avocado, sliced (healthy fats)
- 2 large eggs (protein)
- 1 tablespoon olive oil (healthy fats)
- 1/4 cup cherry tomatoes, halved (fiber, vitamins)
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Optional toppings: Chia seeds (fiber, omega-3s), feta cheese (protein, calcium), fresh herbs (e.g., cilantro or parsley)
Instructions:
- Cook the Quinoa: If not already cooked, rinse 1/2 cup of quinoa under cold water and then cook it according to package instructions. This should take about 15 minutes.
- Sauté the Spinach: In a pan, heat 1 tablespoon of olive oil over medium heat. Add the spinach and sauté for 2-3 minutes until wilted. Remove from heat and set aside.
- Cook the Eggs: You can prepare the eggs according to your preference—poached, scrambled, or fried. For poached eggs, bring a pot of water to a simmer, add a splash of vinegar, and gently crack the eggs into the water. Cook for about 3-4 minutes until the whites are set but the yolks are still runny. For scrambled or fried eggs, cook in a non-stick pan over medium heat.
- Assemble the Bowl: In a serving bowl, layer the cooked quinoa at the bottom. Add the sautéed spinach, sliced avocado, and cherry tomatoes on top.
- Top with Eggs: Place the eggs on top of the bowl.
- Season and Serve: Sprinkle with salt and pepper to taste. Add any optional toppings like chia seeds or feta cheese.
Nutritional Benefits:
- Protein: Eggs and quinoa provide a significant amount of high-quality protein to keep you full and satisfied.
- Fiber: Quinoa, spinach, tomatoes, and avocado all contribute to a high fiber content, which is essential for digestive health and stabilizing blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado and olive oil provide monounsaturated fats that are good for heart health and help in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Lunch and Dinner Recipe that is Blood Sugar Balancing
Grilled Salmon with Lentil and Kale Salad. This dish is both nutritious and satisfying, making it an excellent choice for a healthy lunch or dinner.
Ingredients:
For the Salmon:
- 2 salmon fillets (about 6 oz each) (protein, healthy fats)
- 1 tablespoon olive oil (healthy fats)
- Juice of 1/2 lemon (flavor, vitamin C)
- 1 garlic clove, minced (flavor, antioxidants)
- Salt and pepper to taste
For the Lentil and Kale Salad:
- 1 cup cooked lentils (fiber, protein)
- 2 cups kale, chopped (fiber, vitamins)
- 1/2 avocado, diced (healthy fats, fiber)
- 1/4 cup red onion, finely chopped (fiber, flavor)
- 1/2 cup cherry tomatoes, halved (fiber, vitamins)
- 1 tablespoon olive oil (healthy fats)
- 1 tablespoon balsamic vinegar (flavor)
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Optional toppings: Crumbled feta cheese (protein, calcium), toasted nuts like almonds or walnuts (healthy fats, fiber)
Instructions:
For the Salmon:
- Marinate the Salmon: In a small bowl, mix olive oil, lemon juice, minced garlic, salt, and pepper. Brush this marinade over the salmon fillets and let them sit for about 10-15 minutes to absorb the flavors.
- Grill the Salmon: Preheat your grill or grill pan over medium-high heat. Place the salmon fillets skin-side down and grill for about 4-5 minutes per side, or until the salmon is cooked through and flakes easily with a fork. Set aside.
For the Lentil and Kale Salad:
- Cook the Lentils: If not already cooked, rinse 1 cup of lentils and cook them according to package instructions. This typically takes about 20-25 minutes. Drain and set aside.
- Prepare the Kale: In a large mixing bowl, massage the chopped kale with a small drizzle of olive oil and a pinch of salt for about 2-3 minutes. This helps to soften the kale and reduce its bitterness.
- Combine the Salad: Add the cooked lentils, diced avocado, chopped red onion, and cherry tomatoes to the kale. Drizzle with olive oil and balsamic vinegar, then toss everything together until well combined. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
- Assemble the Dish: Serve the grilled salmon fillets on top of or alongside the lentil and kale salad. Sprinkle with optional toppings like crumbled feta cheese or toasted nuts for added flavor and texture.
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/316427






