Exercise and intentional movement have many well-known benefits. Most people emphasize the weight management benefits, cardiovascular influence as well as muscular strength and endurance. It’s likely you’ve heard about it positively influencing mental health including mood and stress, but it’s possible you haven’t considered some of the largest and most impactful benefits of regular exercise. Movement and physical activity has an incredible influence on our total health. To explain, it helps by starting with an understanding of the hallmarks of health.
The hallmarks of health refer to key principles that support long-term well-being, disease prevention, and vitality. They provide a holistic approach to health, covering biological, lifestyle, and environmental factors. These hallmarks reflect the interconnected nature of health, meaning one area affects the others. They align well with functional medicine principles, focusing on root causes rather than symptoms alone. Let’s take a look at the core hallmarks of your health.
Core Hallmarks of Health
- Metabolic Health
Metabolic health refers to how efficiently our body processes and uses energy from food to sustain vital functions. It involves balanced blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, healthy cholesterol and blood pressure, and optimal energy production. When our metabolism is working well, we feel energized, maintain a stable weight, and experience fewer cravings. However, poor metabolic health can lead to fatigue, weight gain, hormonal imbalances, and an increased risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and metabolic syndromes.
- Hormonal Balance
Hormonal health refers to the delicate balance of hormones that regulate nearly every function in our body, from metabolism and mood to sleep, reproduction, and energy levels. When our hormones are in sync, we feel vibrant, focused, and resilient. However, imbalances—caused by stress, poor nutrition, lack of sleep, or underlying health conditions—can lead to fatigue, weight fluctuations, mood swings, irregular cycles, and other health issues. Hormonal balance includes the proper function of thyroid, adrenal and reproductive hormones.
- Nutrient Sufficiency
Nutrient sufficiency means providing our bodies with the essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients needed to function optimally. When we consume a well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet, our energy levels, metabolism, immune function, and overall health thrive. However, deficiencies—often caused by poor diet, stress, or gut health issues—can lead to fatigue, weakened immunity, brain fog, and other imbalances.
- Gut & Digestive Health
Gut and digestive health play a crucial role in overall well-being, influencing everything from nutrient absorption and immune function to mood and metabolism. A healthy gut relies on a balanced microbiome, strong digestion, and an intact gut lining to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste efficiently. When digestion is compromised—due to stress, poor diet, imbalances in gut bacteria, or food sensitivities—it can lead to bloating, discomfort, fatigue, and even systemic inflammation.
- Inflammation Control
Managing inflammation is essential for maintaining long-term health and preventing chronic disease. While short-term inflammation is a natural response to injury or illness, chronic inflammation—often driven by poor diet, stress, toxins, and lifestyle factors—can contribute to issues like fatigue, weight gain, joint pain, neuro cognitive disease and autoimmune conditions.
- Cellular & Mitochondrial Function
Cellular and mitochondrial health are the foundation of our energy, vitality, and overall well-being. Our cells rely on mitochondria—the “powerhouses” of the cell—to produce ATP, the energy that fuels every function in the body. When mitochondria are healthy, we experience steady energy, mental clarity, and efficient metabolism. However, factors like poor nutrition, toxins, chronic stress, and aging can damage mitochondria, leading to fatigue, brain fog, and increased risk of disease.
- Detoxification & Toxin Reduction
Detoxification is the body’s natural process of eliminating toxins through the liver, kidneys, gut, skin, and lymphatic system. However, modern lifestyles expose us to an overwhelming number of environmental toxins, processed foods, and stressors that can burden these systems, leading to fatigue, hormone imbalances, brain fog, and inflammation.
- Mental & Emotional Well-being
Mental and emotional well-being are vital to overall health, influencing how we think, feel, and navigate daily life. A balanced mind supports resilience, clarity, and emotional stability, while chronic stress, negative thought patterns, and unresolved emotions can contribute to anxiety, fatigue, and even physical health issues.
- Sleep & Circadian Rhythm Health
Sleep and circadian rhythm health are essential for overall well-being, impacting energy, metabolism, hormone balance, and cognitive function. Our circadian rhythm—the body’s internal clock—regulates sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, and cellular repair. Poor sleep habits, exposure to artificial light, and irregular schedules can disrupt this rhythm, leading to fatigue, brain fog, weight gain, and weakened immunity.
- Movement & Physical Activity
Referring to the intentional and consistent lifestyle of activity and movement. It may include strength training workouts, but can also include gardening, active jobs and playing a sport.
Now that we’ve examined the hallmarks of health, let’s discover together why exercise is one of the most powerful tools for optimizing the hallmarks of health, influencing nearly every system in the body. Here’s how it supports each of the core hallmarks of health.
Exercise and the Hallmarks of Health
1. Exercise and Metabolic Health
Exercise plays a crucial role in improving metabolic health by enhancing insulin sensitivity, which helps lower blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It also boosts mitochondrial function, increasing energy production at the cellular level, leading to more sustained energy throughout the day. Additionally, regular physical activity accelerates fat metabolism, aiding in weight management and preventing excess fat storage. This combination of benefits helps prevent metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and obesity—conditions that can lead to serious health complications. By incorporating exercise into our routine, we support a healthier metabolism and reduce our risk of chronic disease.
💡 Why it matters: Helps prevent metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
2. Exercise and Hormonal Balance
Exercise significantly improves hormonal health by lowering cortisol, the stress hormone, which helps reduce the negative effects of chronic stress on the body, such as fatigue and anxiety. It also stimulates the production of testosterone and growth hormone, which support muscle growth, recovery, and overall strength. Additionally, regular physical activity improves thyroid function, helping to regulate metabolism and energy levels. This combination of benefits promotes balanced energy, improved mood, and overall hormonal harmony, which is essential for optimal physical and mental health.
💡 Why it matters: Supports balanced energy, mood, and overall hormonal health.
3. Exercise and Nutrient Sufficiency
Exercise improves nutrient sufficiency by enhancing nutrient absorption, which supports better digestion and gut function. Regular physical activity increases the body’s demand for essential nutrients, encouraging healthier dietary choices to meet those needs. This heightened nutrient demand promotes a more balanced and nutrient-dense diet, ensuring the body receives the vitamins and minerals it requires. Additionally, exercise helps reduce oxidative stress, which can damage cells, by improving the body’s antioxidant defenses. This combination of benefits supports overall cellular health, protects against chronic disease, and optimizes the body’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients efficiently.
💡 Why it matters: Ensures the body efficiently utilizes nutrients for optimal function.
4. Exercise and Gut & Digestive Health
Exercise offers numerous benefits for gut and digestive health by supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Regular physical activity increases the diversity of beneficial bacteria, which is essential for maintaining a balanced microbiome and optimal digestion. It also enhances digestive motility, helping to move food more efficiently through the digestive tract and preventing issues like bloating and constipation. Additionally, exercise helps lower gut inflammation, reducing the risk of conditions like leaky gut and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). By promoting a healthier gut environment, exercise supports better digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut function.
💡 Why it matters: A healthy gut improves immunity, mental health, and metabolism.
5. Exercise and Inflammation Control
Exercise plays a powerful role in controlling inflammation by reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory markers in the body. Regular physical activity helps to lower chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, arthritis, and metabolic disorders. By promoting the production of anti-inflammatory proteins and improving circulation, exercise reduces the overall inflammatory load, allowing the body to recover more effectively from stress and injury. This ability to control inflammation is key for long-term health, as it helps protect the body from chronic conditions and supports a more balanced, resilient system.
💡 Why it matters: Chronic inflammation is linked to heart disease, cancer, and aging.
6. Exercise and Cellular & Mitochondrial Function
Exercise stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, which boosts energy production at the cellular level by creating more mitochondria to meet the body’s increased energy demands. This not only enhances energy levels but also improves overall endurance and physical performance. Additionally, exercise increases autophagy, the body’s process of cellular cleanup, which removes damaged or dysfunctional cells and promotes healthier, more efficient cellular function. It also enhances oxygen delivery to tissues, improving recovery times and endurance during physical exertion. Together, these effects support better mitochondrial function, quicker recovery, and greater overall vitality.
💡 Why it matters: Stronger cells mean better energy, longevity, and disease prevention.
7. Exercise and Detoxification & Toxin Reduction
Exercise plays a vital role in detoxification by promoting lymphatic drainage and sweating, both of which help eliminate toxins from the body. As we sweat, we release not only excess heat but also harmful substances like heavy metals and environmental toxins. Regular physical activity also supports liver and kidney function, key organs involved in detoxifying the body, by enhancing their ability to process and remove waste. Additionally, exercise can help reduce the exposure to toxins stored in fat cells, as fat-burning activity encourages the release of these stored toxins into the bloodstream, where they can be processed and eliminated. This combination of benefits ensures more effective detoxification, leading to better overall health and a reduction in the toxic burden on the body.
💡 Why it matters: Helps clear out environmental toxins and metabolic waste.
8. Exercise and Mental & Emotional Well-being
Exercise has a profound impact on mental and emotional well-being by increasing the production of dopamine and serotonin, two key neurotransmitters that play a crucial role in mood regulation. This boost in feel-good chemicals helps improve mood, increase motivation, and combat feelings of sadness or lethargy. Regular physical activity also lowers the risk of anxiety and depression by reducing stress hormones like cortisol and promoting relaxation. Additionally, exercise enhances mental clarity and strengthens brain health by stimulating neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and form new neural connections. This combination of benefits supports better cognitive function, emotional resilience, and a more positive outlook on life.
💡 Why it matters: Regular movement improves resilience, focus, and overall well-being.
9. Exercise and Sleep & Circadian Rhythm Health
Exercise has a powerful impact on sleep by regulating melatonin production, a hormone that helps signal to the body when it’s time to sleep. As a result, physical activity improves overall sleep quality, allowing for deeper, more restorative rest. Regular exercise also helps synchronize the body’s circadian rhythm, aligning sleep-wake cycles with natural light patterns, which boosts energy levels during the day and promotes a more restful night. Additionally, exercise can reduce restlessness and sleep disturbances by relieving stress, lowering anxiety, and improving relaxation, leading to more consistent and rejuvenating sleep.
💡 Why it matters: Better sleep enhances healing, memory, and immune function.
10. Movement & Physical Activity
Exercise provides numerous physical benefits that are essential for long-term health and vitality. It increases muscle strength and endurance, which helps prevent frailty as we age by maintaining mobility and functional strength. Regular physical activity also improves bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures by stimulating bone-building processes. Additionally, exercise supports cardiovascular health by enhancing circulation, lowering blood pressure, and improving cholesterol levels, which in turn lowers the risk of heart disease. These combined benefits help to build a resilient body, prevent age-related decline, and promote overall longevity and well-being.
💡 Why it matters: A strong, functional body leads to a longer, healthier life.
Exercise is a largely underestimated and underutilized tool in preventing many health issues as well as diminishing their effects when already experiencing them. Science has shown time and time again that exercise has ripple effects on improving our overall health. The best part is that it’s free! Here are some other lesser known benefits!
- Improved Cognitive Function: Regular physical activity has been shown to enhance brain plasticity, helping with memory retention, learning, and even creativity.
- Enhanced Sensory Processing: Movement helps to improve the way your brain processes sensory information, making you more attuned to your surroundings and better at multitasking.
- Increased Self-Esteem: Beyond just physical appearance, movement can boost your sense of accomplishment and competence, improving your self-worth over time.
- Emotional Resilience: Exercise helps regulate emotions by promoting the release of endorphins and serotonin, which can help buffer against stress and anxiety.
- Improved Posture: Regular movement strengthens the muscles that support your spine, leading to better posture and less discomfort, especially in a sedentary world.
- Better Immune Function: Moderate movement has been linked to better immune response, making your body more capable of fighting off infections.
- Increased Emotional Intelligence: Regular physical activity helps increase awareness of your body and emotions, which can enhance emotional intelligence and interpersonal relationships.
- Enhanced Social Connections: Moving in group settings or sports can improve your sense of community, build teamwork skills, and create lasting bonds that help with mental well-being.
- Boosted Creativity and Problem-Solving: Engaging in physical activity can unlock new ways of thinking, as it allows your mind to wander and make creative connections that you might miss when sedentary.
Exercise is a cornerstone of health, positively influencing every major system in the body. Whether it’s strength training, cardio, yoga, or simply moving more, physical activity is one of the best ways to improve all hallmarks of health.
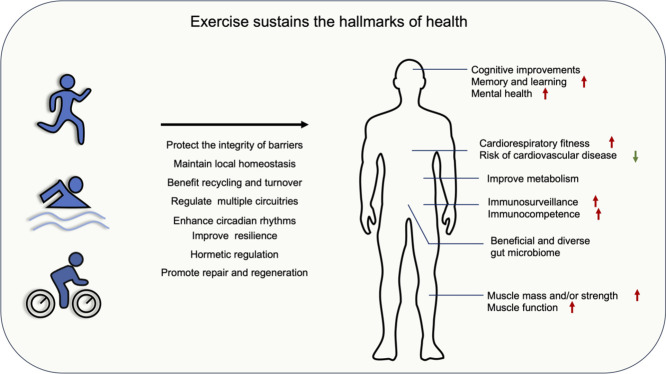
Image taken from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9923435/figure/fig0008
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/gut-health-workout
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11133400
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9923435
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9923435/figure/fig0008






